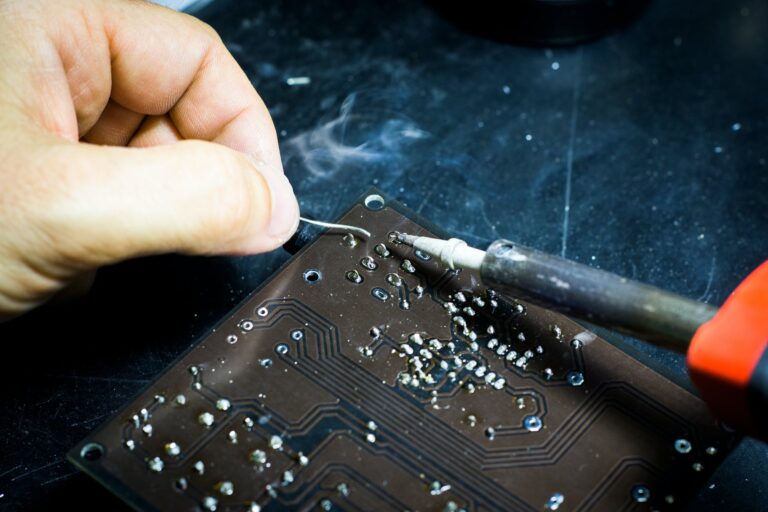
PCBs have come a long way from their earliest days up until today. Everything about them has become far more advanced and sophisticated, including the assembly process. Now, the assembly process is not as complicated as some may think, but you still need to know some basics if you want to get into it. So, if that’s the case – here’s what you need to know.
-
Not All PCBs Are The Same
The assembly process will slightly vary from one circuit board to another, primarily because there are different kinds of PCBs.
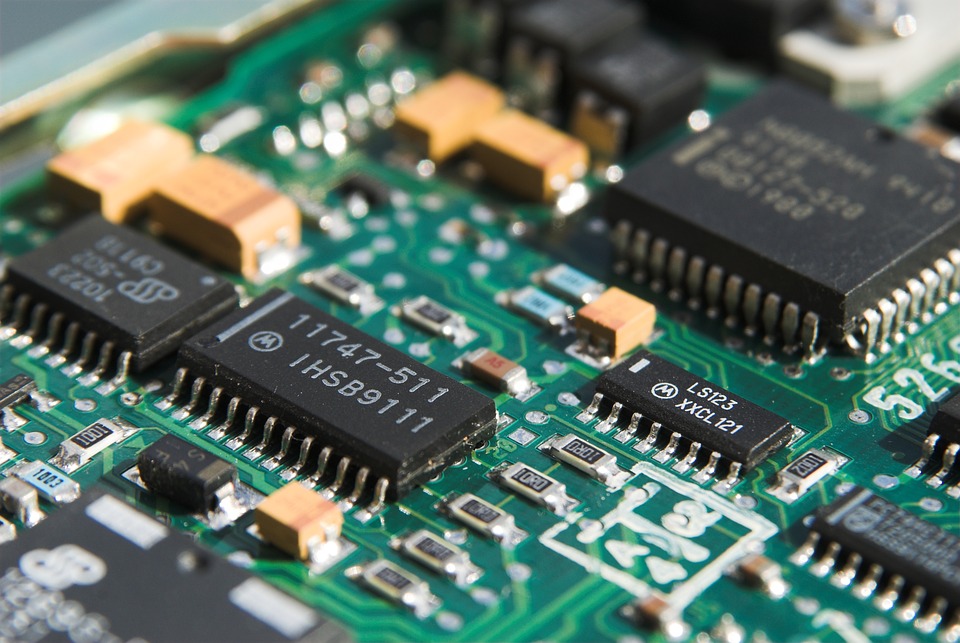
A PCB is usually made from 4 parts – a substrate, copper layers, a solder mask, and a silkscreen. Based on substrate material alone, there are three types of PCBs – rigid (the majority of all circuit boards are rigid), flexible (usually the ones found in wearable electronics or connectors,) and metalcore PCBs (used for heat-sensitive components).
-
There Are Two Main Mounting Technologies
When it comes to mounting the components to the circuit board, there are two main mounting techniques – SMT and THT.
SMT stands for “Surface Mount Technology” and is usually includes mounting really tiny components. Because of it, most of this is done by machinery instead of by hand. THT or “Through-hole Technology“, on the other hand, is reserved for slightly bulkier components, where you’d insert a component from one side of the PCB and pull it out from another. Generally, THT is done by hand.
-
DFM Always Comes First
Before even attempting the assembly, a PCB must undergo a thorough inspection or “Design for manufacturing” process. According to Vinatronic, a PCB Assembly company, during this inspection, the circuit board will be checked for various defects to make sure everything is up to code so that a circuit board can be assembled.
-
Design Is As Important As The Assembly
To fit all these components onto a small circuit board and have them all perform the way they should is a lot easier said than done. No matter how important the assembly process is, unless designed properly, a circuit board won’t be operable no matter how great of a job you do assembling it. So, pay special attention and put a lot of effort into the design of the PCB, and only then worry about assembly.
-
The Process Is Simpler Than You Might Think
Every assembly process starts with the application of the solder paste on the areas of the board where the components will be added. After the solder paste has been applied, it is time to place to components with the help of a robot. The third step would be reflowing the soldering, which would firmly place the components in place via the melting and cooling process. After all of that is done, the PCB undergoes a thorough inspection. An inspection can be either manual or automated. After inspection, the functional test is performed, and if the PCB proves to be in perfect condition – they’re good to go.
Conclusion
Naturally, performing any of these requires a lot of knowledge and expertise, but essentially – that’s pretty much all there is to. Hopefully, you’ve found this helpful.

