https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hJ-P8jyuB5E
QUESTIONS 35-39
35. What is the main purpose of the conversation?
(A) The professor asked the student to come and talk to him.
(B) The professor wants the student to be his teaching assistant.
(C) The student wants a recommendation from the professor.
(D) The student wants to discuss her research project.
36. Why does the student want to be a teacher?
(A) She has an opportunity to teach a class about nature.
(B) She enjoyed studying science when she was a child.
(C) She is interested in the psychology of children’s art.
(D) She wants to make the professor proud of her.
37. Why does the student talk about being a camp counselor?
(A) To summarize what she did in a psychology course
(B) To describe her experience in working with children
(C) To explain her interest in being a psychologist
(D) To ask for the professor’s help in getting a job
38. Listen again to part of the conversation. Then answer the question.
Why does the professor say this:
(T) He is thinking about what he will say in the recommendation.
(T) He wants to know the student’s opinion of his psychology class.
(T) He needs the student’s help in solving a difficult problem.
(T) He would like to try something that he has never done before.
39. What will the professor probably include in the form that he fills out?
A. The student’s examination scores
B. Slides of the student’s artwork
C. A copy of the student’s employment history
D. A description of the student’s research report
QUESTIONS 40-45
40. What is the main purpose of the lecture?
(A) To trace the natural history of Manitoba’s Interlake region
(B) To describe the process of limestone formation
(C) To explain how one animal survives in its environment
(D) To persuade students that snakes are not dangerous
41. What natural features of Manitoba does the professor discuss?
Click on two answers.
[a] The large number of lakes
[b] The network of limestone caves
[c] The concentration of garter snakes
[d] The variety of snake species
42. Why does the professor say this:
(A) To praise the area’s beautiful winter scenery
(B) To persuade students to build their own homes
(C) To describe the most common use of limestone
(D) To explain why so many snakes live in the region
43. How do the garter snakes deal with seasonal variations in temperature?
(A) They grow an extra layer of skin in winter and shed it in summer.
(B) They survive by migrating toward the south every winter.
(C) They move into the limestone pits to escape winter temperatures.
(D) They vary their food intake to maintain a constant body temperature.
44. Listen again to part of the lecture. Then answer the question.
What does the professor mean when he says this: Q
(A) The snakes come out of their dens every morning.
(B) The snakes can survive a night of freezing temperatures.
(C) The snakes will stay frozen until all danger has passed.
(D) The snakes are least active during the night.
45. Listen again to part of the lecture. Then answer the question.
What does the professor imply about the behavior of the snakes?
(A) The snakes’ behavior is a warning signal to other animals.
(B) Temperature plays an important role in the snakes’ behavior.
(C) Scientists can observe the snakes’ behavior in their winter dens.
(D) The snakes are able to learn a variety of behavioral responses.
QUESTIONS 46-51
46. According to the professor, why was the arch an important development in architecture?
Click on two answers.
A. The arch made Rome the greatest power on Earth.
B. Wide openings could be spanned without using wood.
C. There was no formal architecture before the arch.
D. The arch led to a larger variety of buildings.
47. Listen again to part of the lecture. Then answer the question.
What does the professor imply about the public works projects of the Romans?
A. The arch contributed to the success of these projects.
B. The Romans were the first society to work on large projects.
C. Each project developed a different style of architecture.
D. The projects benefited only the wealthy citizens of Rome.
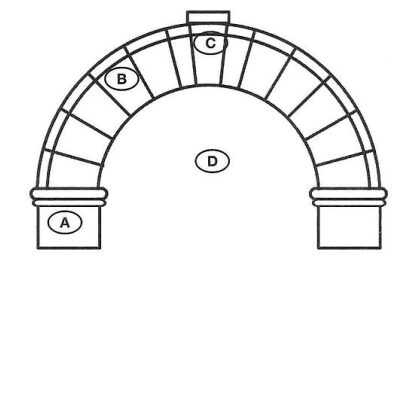
48. Identify the keystone in the drawing of the arch.
49. What reason is given for the stability of the arch?
(A) A concrete foundation supports the arch.
(B) The arch is built with wedge-shaped blocks.
(C) The Romans made a strong type of concrete.
(D) The pressure flows up to the keystone.
50. Listen again to part of the lecture. Then answer the question.
Why does the professor say this:
(A) To describe the shape of the arch
(B) To define the concept of lateral thrust
(C) To compare two types of physical force
(D) To explain why arches must be large
51. According to the professor, why are arches that are built today mostly decorative in function?
A. Wedge-Shaped blocks have become rare.
B. Decorative arches provide work for bricklayers.
C. Few architects like ancient construction techniques.
D. Wide openings are now spanned with steel hen ms